Task 4: Implement CRUD Operations
In this task, we will update the UI to facilitate CRUD operations for the posts app. We will use the API calls we created in the previous task to fetch, create, update, and delete posts.
Step 1: Read all posts
Let’s start by updating the Posts component to fetch all posts from the API and display them in the UI. Currently, we are using a static list of posts from the data/db.json file. We will replace this with an API call to fetch the posts.
- import { useState } from "react";
+ import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import Post from "./post";
- import db from "@/data/db.json";
+ import { fetchPosts } from "@/data/api";
const Posts = () => {
- const [posts, setPosts] = useState<PostType[]>(db.posts);
+ const [posts, setPosts] = useState<PostType[]>([]);
+ useEffect(() => {
+ fetchPosts().then((data) => setPosts(data));
+ }, []);
return (
<div>
{posts
.sort((a, b) => (a.date > b.date ? -1 : 1))
.map((post) => (
<Post key={post.id} post={post} />
))}
</div>
);
};
export default Posts;When the component mounts, we fetch the posts from the API and update the state with the fetched data.
Step 2: Delete a post
When you click on the trash icon, we want to trigger the deletion of the corresponding post. To achieve this, we’ll call the deletePost function, which makes an API request to remove the post from the list.
To execute the deletePost function, we need to pass the unique identifier (post.id) as an argument. To do this, we can pass the entire post object as a prop to the PostActions component, allowing us to access and use the id property when needed.
First, update the Post component to pass the post object to the PostActions component.
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import PostActions from "./post-actions";
const Post = ({ post }: { post: PostType }) => {
return (
<div className="p-1 border-b">
<div className="flex items-center justify-between pl-4">
<div className="text-xs text-muted-foreground">
{new Date(post.date).toLocaleString("en-US", {
month: "short",
day: "numeric",
year: "numeric",
hour: "numeric",
minute: "numeric",
})}
</div>
- <PostActions />
+ <PostActions post={post} />
</div>
<p className="p-4">{post.content}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default Post;Next, update the PostActions component to accept the post object as a prop and call the deletePost function when the trash icon is clicked.
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
+ import { deletePost } from "@/data/api";
+ import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import { TrashIcon, Pencil2Icon } from "@radix-ui/react-icons";
- const PostActions = () => {
+ const PostActions = ({ post }: { post: PostType }) => {
return (
<div className="flex justify-end">
<Button variant={"ghost"} size={"icon"}>
<Pencil2Icon className="w-4 h-4" />
</Button>
<Button
variant={"ghost"}
size={"icon"}
+ onClick={() => deletePost(post.id)}
>
<TrashIcon className="w-4 h-4" />
</Button>
</div>
);
};
export default PostActions;Run the program and click on the trash icon next to one of the posts. You’ll notice that it doesn’t disappear from the list immediately. To verify, check the api/db.json file to see that the post has indeed been deleted from the “database.” However, the UI still displays the old list of posts because we haven’t updated the state to reflect the changes. You can refresh the page to see the updated list of posts.
To make this behavior more efficient, we don’t want to require a page refresh to see the changes. Instead, we can update the state of our posts directly. To achieve this, let’s pass the setPosts function from the Posts component down to the Post component, and then further down to the PostActions component. This will enable us to update the state directly when a post is deleted, without having to re-fetch the entire list of posts.
First, update the Posts component to pass the setPosts function to the Post component.
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import Post from "./post";
import { fetchPosts } from "@/data/api";
const Posts = () => {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState<PostType[]>([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetchPosts().then((data) => setPosts(data));
}, []);
return (
<div>
{posts
.sort((a, b) => (a.date > b.date ? -1 : 1))
.map((post) => (
- <Post key={post.id} post={post} />
+ <Post key={post.id} post={post} setPosts={setPosts} />
))}
</div>
);
};
export default Posts;Next, update the Post component to pass the setPosts function to the PostActions component.
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import PostActions from "./post-actions";
type PostProps = {
post: PostType;
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
};
const Post = ({ post, setPosts }: PostProps) => {
return (
<div className="p-1 border-b">
<div className="flex items-center justify-between pl-4">
<div className="text-xs text-muted-foreground">
{new Date(post.date).toLocaleString("en-US", {
month: "short",
day: "numeric",
year: "numeric",
hour: "numeric",
minute: "numeric",
})}
</div>
<PostActions post={post} setPosts={setPosts} />
</div>
<p className="p-4">{post.content}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default Post;Finally, update the PostActions component to call the setPosts function after deleting a post.
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { deletePost } from "@/data/api";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import { TrashIcon, Pencil2Icon } from "@radix-ui/react-icons";
type PostActionsProps = {
post: PostType;
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
};
const PostActions = ({ post, setPosts }: PostActionsProps) => {
const handleDelete = async () => {
await deletePost(post.id);
setPosts((prevPosts: PostType[]) =>
prevPosts.filter((p: PostType) => p.id !== post.id),
);
};
return (
<div className="flex justify-end">
<Button variant={"ghost"} size={"icon"}>
<Pencil2Icon className="w-4 h-4" />
</Button>
<Button variant={"ghost"} size={"icon"} onClick={handleDelete}>
<TrashIcon className="w-4 h-4" />
</Button>
</div>
);
};
export default PostActions;Now if you delete a post by clicking on the trash icon, it will be removed from the list without having to refresh the page.
Notice how we use the setPosts function to update the state of the posts. Instead of directly passing the new list of posts, we pass a function that receives the previous state and returns the new state. This enables us to filter out the post that was deleted from the list of posts.
Moreover, notice the type of the setPosts function. It is React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>. We are using the type React.Dispatch to define the type of the function that can be used to update the state. The React.SetStateAction type is a utility type provided by React that represents the type of the state setter function. In this case, it is a function that takes the previous state as an argument and returns the new state.
Step 3: Add confirmation dialog
It is possible that a user might accidentally click on the trash icon and delete a post. To prevent this, we can add a confirmation dialog before deleting a post.
To achieve this, we will use an alert dialog component that will display a confirmation message before deleting the post. The shadcn UI library provides an AlertDialog component that we can use for this purpose.
pnpm dlx shadcn@latest add alert-dialogCreate a new component delete-post-dialog.tsx in the components folder.
import {
AlertDialog,
AlertDialogAction,
AlertDialogCancel,
AlertDialogContent,
AlertDialogDescription,
AlertDialogFooter,
AlertDialogHeader,
AlertDialogTitle,
AlertDialogTrigger,
} from "@/components/ui/alert-dialog";
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { TrashIcon } from "@radix-ui/react-icons";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import { deletePost } from "@/data/api";
type DeletePostDialogProps = {
post: PostType;
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
};
const DeletePostDialog = ({ post, setPosts }: DeletePostDialogProps) => {
const handleDelete = async () => {
await deletePost(post.id);
setPosts((prevPosts: PostType[]) =>
prevPosts.filter((p: PostType) => p.id !== post.id),
);
};
return (
<AlertDialog>
<AlertDialogTrigger asChild>
<Button variant={"ghost"} size={"icon"}>
<TrashIcon className="w-4 h-4" />
</Button>
</AlertDialogTrigger>
<AlertDialogContent>
<AlertDialogHeader>
<AlertDialogTitle>Are you absolutely sure?</AlertDialogTitle>
<AlertDialogDescription>
This action cannot be undone. This will permanently delete your post
and remove it from our servers.
</AlertDialogDescription>
</AlertDialogHeader>
<AlertDialogFooter>
<AlertDialogCancel>Cancel</AlertDialogCancel>
<AlertDialogAction onClick={handleDelete}>Continue</AlertDialogAction>
</AlertDialogFooter>
</AlertDialogContent>
</AlertDialog>
);
};
export default DeletePostDialog;Notice the AlertDialog component from the shadcn UI library. It provides a way to display an alert dialog with a title, description, and action buttons. The AlertDialogTrigger component is used to trigger the alert dialog. In this case, we are using a button with the trash icon as the trigger. The AlertDialogContent component contains the content of the alert dialog, including the title, description, and action buttons. The AlertDialogAction component is used to define the action button that will be triggered when clicked. In this case, we are calling the handleDelete function to delete the post. The AlertDialogCancel component is used to define the cancel button that will close the alert dialog.
The asChild prop on the AlertDialogTrigger component is a pattern used in Radix UI which Shadcn UI is built on. This prop delegates the rendering of a component to its single child element. In the case of the AlertDialogTrigger component, this allows us to use any element as the trigger for the alert dialog. For a deeper understanding of how asChild works, I recommend reading this article: asChild in React, Svelte, Vue, and Solid for render delegation.
Update the PostActions component to use the DeletePostDialog component.
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
- import { deletePost } from "@/data/api";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
- import { TrashIcon, Pencil2Icon } from "@radix-ui/react-icons";
+ import { Pencil2Icon } from "@radix-ui/react-icons";
+ import DeletePostDialog from "./delete-post-dialog";
type PostActionsProps = {
post: PostType;
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
};
const PostActions = ({ post, setPosts }: PostActionsProps) => {
- const handleDelete = async () => {
- await deletePost(post.id);
- setPosts((prevPosts: PostType[]) =>
- prevPosts.filter((p: PostType) => p.id !== post.id),
- );
- };
return (
<div className="flex justify-end">
<Button variant={"ghost"} size={"icon"}>
<Pencil2Icon className="w-4 h-4" />
</Button>
- <Button variant={"ghost"} size={"icon"} onClick={handleDelete}>
- <TrashIcon className="w-4 h-4" />
- </Button>
+ <DeletePostDialog post={post} setPosts={setPosts} />
</div>
);
};
export default PostActions;Now if you click on the trash icon, an alert dialog will appear asking you to confirm the deletion of the post. If you click on “Continue,” the post will be deleted. If you click on “Cancel,” the post will not be deleted.
Step 4: Create a new post
Let’s add a form to create a new post. We will create a new component add-post.tsx in the components folder. We will use the Textarea and Button components from the shadcn UI library.
pnpm dlx shadcn@latest add textarea labelAdd the following code to the add-post.tsx file.
import { useState } from "react";
import { Textarea } from "@/components/ui/textarea";
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { Label } from "@/components/ui/label";
import { createPost } from "@/data/api";
const AddPost = () => {
const [content, setContent] = useState("");
const handleTextChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLTextAreaElement>) => {
setContent(e.target.value);
};
const handleSave = async (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (content) {
await createPost(content);
setContent("");
}
};
const handleCancel = () => {
setContent("");
};
return (
<form className="grid w-full gap-1.5 p-4 border-b">
<Label htmlFor="content" className="text-sm">
Your post
</Label>
<Textarea
id="content"
placeholder="Type your message here."
value={content}
onChange={handleTextChange}
/>
<div className="flex justify-end gap-3">
<Button type="reset" variant={"secondary"} onClick={handleCancel}>
Cancel
</Button>
<Button type="submit" onClick={handleSave}>
Post
</Button>
</div>
</form>
);
};
export default AddPost;We can add the AddPost component to the Feed component, before displaying the list of posts.
+ import AddPost from "./add-post";
import Header from "./header";
import Posts from "./posts";
const Feed = () => {
return (
<div className="flex flex-col w-full min-h-screen border-x">
<Header />
+ <AddPost />
<Posts />
</div>
);
};
export default Feed;Now if you run the program, you will see the form to create a new post. However, if you add a new post, it will not be displayed in the list of posts. This is because we are not updating the state of the posts to reflect the changes.
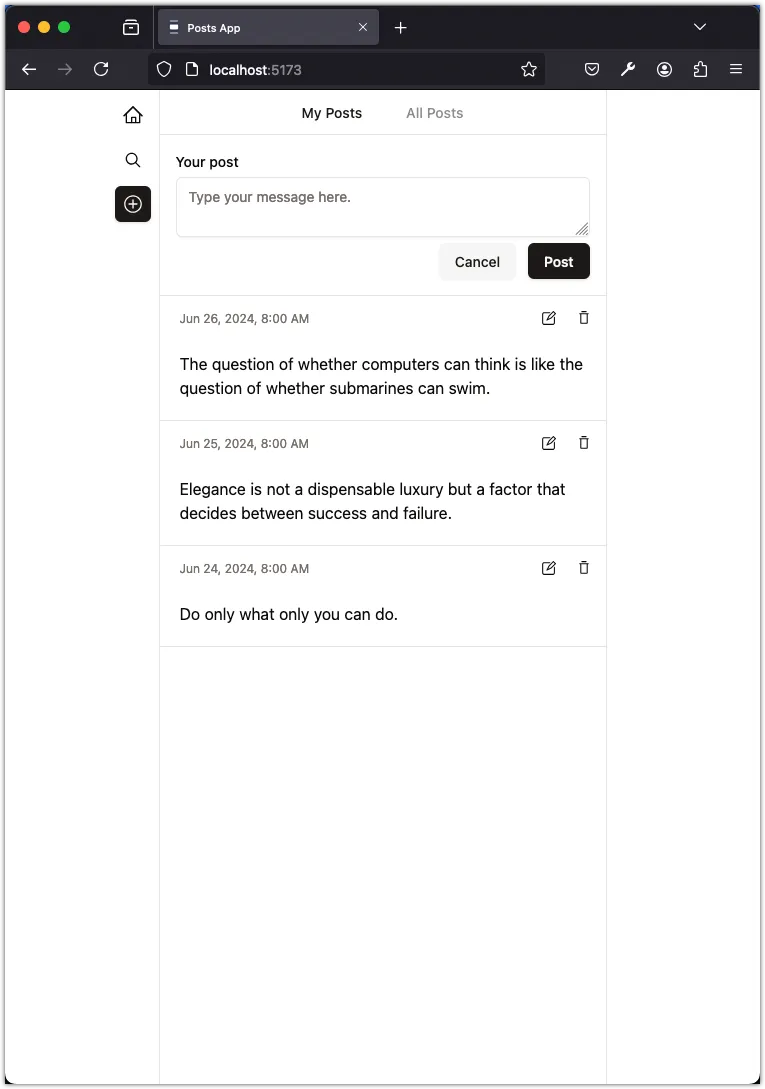
However, if you refresh the page, you will see the new post. In the next step, we will update the state of the posts to reflect the changes when a new post is added.
Step 5: Lift up the state
To update the state of the posts when a new post is added, we need to lift up the state from the Posts component to the Feed component. We will pass the setPosts function to the AddPost component and update the state when a new post is created.
import { useState } from "react";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import AddPost from "./add-post";
import Header from "./header";
import Posts from "./posts";
const Feed = () => {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState<PostType[]>([]);
return (
<div className="flex flex-col w-full min-h-screen border-x">
<Header />
<AddPost setPosts={setPosts} />
<Posts posts={posts} setPosts={setPosts} />
</div>
);
};
export default Feed;Update the Posts component to accept the posts data and setPosts function as props.
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import Post from "./post";
import { fetchPosts } from "@/data/api";
type PostsActionsProps = {
posts: PostType[];
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
};
const Posts = ({ posts, setPosts }: PostsActionsProps) => {
useEffect(() => {
fetchPosts().then((data) => setPosts(data));
// eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps
}, []);
return (
<div>
{posts
.sort((a, b) => (a.date > b.date ? -1 : 1))
.map((post) => (
<Post key={post.id} post={post} setPosts={setPosts} />
))}
</div>
);
};
export default Posts;Notice I added the line // eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps to disable the exhaustive-deps rule for this effect. This is because the setPosts function is not a dependency of the effect, and we don’t want to trigger the effect every time setPosts changes. However, ESLint will warn you about this. You can disable the warning for this line by adding the comment. Be cautious when disabling this rule, as it can lead to bugs if not handled properly.
Next, update the AddPost component to accept the setPosts function as a prop and update the state when a new post is created.
import { useState } from "react";
import { Textarea } from "@/components/ui/textarea";
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { Label } from "@/components/ui/label";
import { createPost } from "@/data/api";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
type AddPostProps = {
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
};
const AddPost = ({ setPosts }: AddPostProps) => {
const [content, setContent] = useState("");
const handleTextChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLTextAreaElement>) => {
setContent(e.target.value);
};
const handleSave = async (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (content) {
const post = await createPost(content);
setPosts((prevPosts) => [post, ...prevPosts]);
setContent("");
}
};
const handleCancel = () => {
setContent("");
};
return (
<form className="grid w-full gap-1.5 p-4 border-b">
<Label htmlFor="content" className="text-sm">
Your post
</Label>
<Textarea
id="content"
placeholder="Type your message here."
value={content}
onChange={handleTextChange}
/>
<div className="flex justify-end gap-3">
<Button type="reset" variant={"secondary"} onClick={handleCancel}>
Cancel
</Button>
<Button type="submit" onClick={handleSave}>
Post
</Button>
</div>
</form>
);
};
export default AddPost;Notice in handleSave, we are calling the createPost function to create a new post. Once the post is created successfully, we update the state of the posts by adding the new post to the list.
Now if you add a new post, it will be added to the list without having to refresh the page.
Step 6: Hide the add post form
It would make sense to hide the add post form when not in use. Let’s add a state to show or hide the add post form. Do this in the App component because we need to share this state with the Sidebar and Feed components. Make sure to pass the showAddPost and setShowAddPost function to the Sidebar and Feed components.
import Sidebar from "@/components/sidebar";
import Feed from "@/components/feed";
import { useState } from "react";
function App() {
const [showAddPost, setShowAddPost] = useState<boolean>(false);
return (
<div className="flex min-h-dvh">
<div className="flex-1 min-w-14">
<Sidebar showAddPost={showAddPost} setShowAddPost={setShowAddPost} />
</div>
<div className="w-full max-w-md mx-auto md:max-w-lg">
<Feed showAddPost={showAddPost} setShowAddPost={setShowAddPost} />
</div>
<div className="flex-1">{/* Placeholder for another sidebar */}</div>
</div>
);
}
export default App;Update the Sidebar component to show the add post button when the showAddPost state is false (i.e., the add post form is not visible). Moreover, when this button is clicked, it should call the setShowAddPost function to show the add post form.
import {
HomeIcon,
MagnifyingGlassIcon,
PlusCircledIcon,
} from "@radix-ui/react-icons";
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
type SidebarProps = {
showAddPost: boolean;
setShowAddPost: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>;
};
const Sidebar = ({ showAddPost, setShowAddPost }: SidebarProps) => {
return (
<div className="flex flex-col items-end p-2 space-y-2">
<Button aria-label={"Home"} variant="ghost" size="icon">
<HomeIcon className="w-5 h-5" />
</Button>
<Button aria-label={"Search"} variant="ghost" size="icon">
<MagnifyingGlassIcon className="w-5 h-5" />
</Button>
{!showAddPost && (
<Button
aria-label={"Make a Post"}
variant="default"
size="icon"
onClick={() => setShowAddPost(true)}
>
<PlusCircledIcon className="w-5 h-5" />
</Button>
)}
</div>
);
};
export default Sidebar;Now, update the Feed component to show or hide the add post form based on the showAddPost state. Moreover, pass the setShowAddPost function to the AddPost component.
import { useState } from "react";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import AddPost from "./add-post";
import Header from "./header";
import Posts from "./posts";
type FeedProps = {
showAddPost: boolean;
setShowAddPost: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>;
};
const Feed = ({ showAddPost, setShowAddPost }: FeedProps) => {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState<PostType[]>([]);
return (
<div className="flex flex-col w-full min-h-screen border-x">
<Header />
{showAddPost && (
<AddPost setPosts={setPosts} setShowAddPost={setShowAddPost} />
)}
<Posts posts={posts} setPosts={setPosts} />
</div>
);
};
export default Feed;Finally, update the AddPost component to hide the form (change the showAddPost state) when the post or cancel buttons are clicked.
import { useState } from "react";
import { Textarea } from "@/components/ui/textarea";
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { Label } from "@/components/ui/label";
import { createPost } from "@/data/api";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
type AddPostProps = {
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
setShowAddPost: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>;
};
const AddPost = ({ setPosts, setShowAddPost }: AddPostProps) => {
const [content, setContent] = useState("");
const handleTextChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLTextAreaElement>) => {
setContent(e.target.value);
};
const handleSave = async (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (content) {
const post = await createPost(content);
setPosts((prevPosts) => [post, ...prevPosts]);
setContent("");
setShowAddPost(false);
}
};
const handleCancel = () => {
setContent("");
setShowAddPost(false);
};
return (
<form className="grid w-full gap-1.5 p-4 border-b">
<Label htmlFor="content" className="text-sm">
Your post
</Label>
<Textarea
id="content"
placeholder="Type your message here."
value={content}
onChange={handleTextChange}
/>
<div className="flex justify-end gap-3">
<Button type="reset" variant={"secondary"} onClick={handleCancel}>
Cancel
</Button>
<Button type="submit" onClick={handleSave}>
Post
</Button>
</div>
</form>
);
};
export default AddPost;Now, the add post form will be hidden when not in use and will be displayed when the “Make a Post” button is clicked. Moreover, the form will be hidden when a new post is created or when the cancel button is clicked.
Step 7: Update a post
We will use a form similar to the add post form to update a post. Let’s create a new component edit-post.tsx in the components folder to edit a post.
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { Textarea } from "@/components/ui/textarea";
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { Label } from "@/components/ui/label";
import { editPost } from "@/data/api";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
type EditPostProps = {
post: PostType;
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
setIsEditing: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>;
};
const EditPost = ({ post, setPosts, setIsEditing }: EditPostProps) => {
const [id, setId] = useState("");
const [content, setContent] = useState("");
useEffect(() => {
if (post && post.id !== id && post.content !== content) {
setId(post.id);
setContent(post.content);
}
// eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps
}, [post]);
const handleTextChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLTextAreaElement>) => {
setContent(e.target.value);
};
const handleSave = async (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (content) {
await editPost(id, content);
setPosts((prevPosts) =>
prevPosts.map((p) => {
if (p.id === id) {
return { ...p, content: content };
}
return p;
}),
);
setContent("");
setIsEditing(false);
}
};
const handleCancel = () => {
setContent("");
setIsEditing(false);
};
return (
<form className="grid w-full gap-1.5 p-4 border-b">
<Label htmlFor="content" className="text-sm">
Your post
</Label>
<Textarea
id="content"
placeholder="Type your message here."
value={content}
onChange={handleTextChange}
/>
<div className="flex justify-end gap-3">
<Button type="reset" variant={"secondary"} onClick={handleCancel}>
Cancel
</Button>
<Button type="submit" onClick={handleSave}>
Post
</Button>
</div>
</form>
);
};
export default EditPost;Next, update the Post component to define the isEditing state and show the EditPost component when the isEditing state is true. Pass the setIsEditing function to the EditPost component and the PostActions component.
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import PostActions from "./post-actions";
import EditPost from "./edit-post";
import { useState } from "react";
type PostProps = {
post: PostType;
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
};
const Post = ({ post, setPosts }: PostProps) => {
const [isEditing, setIsEditing] = useState(false);
if (isEditing) {
return (
<EditPost post={post} setPosts={setPosts} setIsEditing={setIsEditing} />
);
}
return (
<div className="p-1 border-b">
<div className="flex items-center justify-between pl-4">
<div className="text-xs text-muted-foreground">
{new Date(post.date).toLocaleString("en-US", {
month: "short",
day: "numeric",
year: "numeric",
hour: "numeric",
minute: "numeric",
})}
</div>
<PostActions
post={post}
setPosts={setPosts}
setIsEditing={setIsEditing}
/>
</div>
<p className="p-4">{post.content}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default Post;Next, update the PostActions component to set the isEditing state to true when the pencil icon is clicked.
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { PostType } from "@/data/types";
import { Pencil2Icon } from "@radix-ui/react-icons";
import DeletePostDialog from "./delete-post-dialog";
type PostActionsProps = {
post: PostType;
setPosts: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<PostType[]>>;
setIsEditing: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>;
};
const PostActions = ({ post, setPosts, setIsEditing }: PostActionsProps) => {
return (
<div className="flex justify-end">
<Button
variant={"ghost"}
size={"icon"}
onClick={() => setIsEditing(true)}
>
<Pencil2Icon className="w-4 h-4" />
</Button>
<DeletePostDialog post={post} setPosts={setPosts} />
</div>
);
};
export default PostActions;Now, if you click on the pencil icon next to a post, the post content will be replaced with a form to edit the post. You can make changes to the post content and click on the “Post” button to save the changes. The post content will be updated without having to refresh the page.
Conclusion
In this task, we implemented CRUD operations for the posts app. We updated the UI to fetch, create, update, and delete posts using API calls. We also added a confirmation dialog before deleting a post and a form to create and edit posts. By lifting up the state and sharing it between components, we were able to update the UI efficiently without requiring a page refresh.